-
Research Article
-
Automated BIM Modeling Based on AI-Generated Imagery - Focusing on Building Façade Wall Pattern Generation and Modeling -
AI 생성 이미지 기반 BIM 모델링 자동화 구현 - 건축물 외관 벽체 패턴 생성 및 모델링을 중심으로 -
-
Youngjin Yoo, Hayoon Kim, Jin-Kook Lee
유영진, 김하윤, 이진국
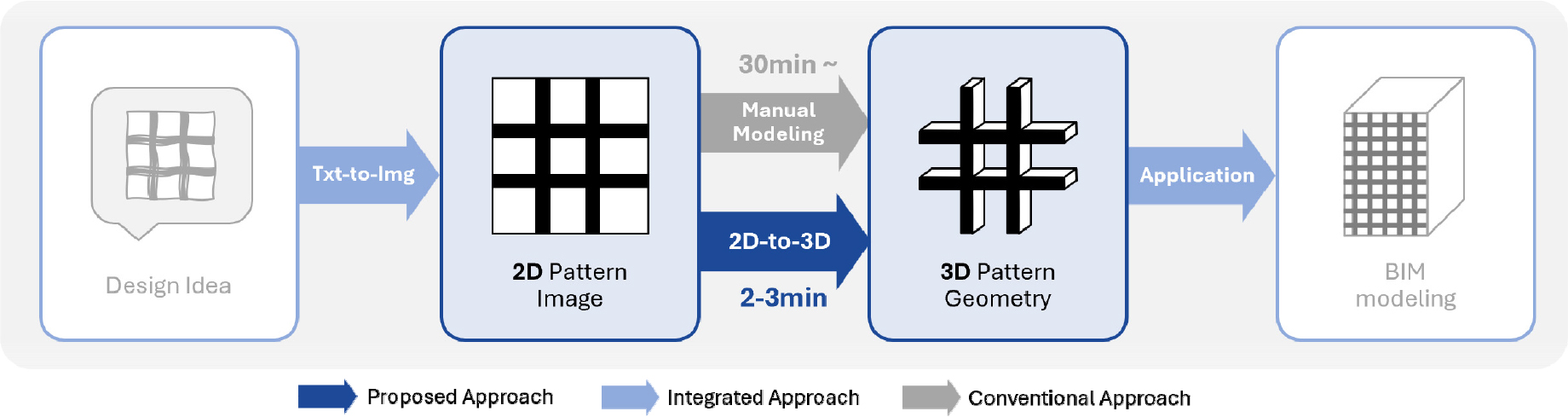
- This study proposes a 2D-to-3D algorithm-based framework for automated BIM modeling of building façade wall patterns generated by image generation AI, reflecting …
- This study proposes a 2D-to-3D algorithm-based framework for automated BIM modeling of building façade wall patterns generated by image generation AI, reflecting diverse design styles, into BIM-compatible 3D models. Initially, façade wall pattern images embodying ten distinct architectural styles were generated using image generation AI. For those styles whose reproduction performance was comparatively low, Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA)-based domain-specific fine-tuning was applied to enhance image quality. As a result, the style similarity measured by CLIPScore for these targeted styles improved significantly from an average of 16.8% to 67.5%. Following this, the proposed 2D-to-3D algorithm processes the generated images through brightness-to-height mapping, vector point preprocessing, and scale adjustment to automatically produce 3D geometries compatible with BIM environments. The converted 3D models demonstrated an average Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM) of 0.71 when compared with the original images, with particularly high fidelity in curve-oriented patterns (up to 0.78). Integrated within a BIM visual programming environment, the system enables users to generate BIM-ready 3D façade wall models from text prompts within 2 to 5 minutes, substantially reducing the time required for pattern creation and design alternative exploration during the early design stages. By extending the creative visualization capabilities of image generation AI into tangible modeling and design execution phases, this framework offers a promising approach to enhance automation and improve efficiency throughout architectural façade design workflows. - COLLAPSE
-
Automated BIM Modeling Based on AI-Generated Imagery - Focusing on Building Façade Wall Pattern Generation and Modeling -
-
Research Article
-
Topic Modeling Analysis of BIM Research Across Design, Construction, and Operation Phases: A 25-Year Time-Series Study Using LDA and BERTopic
BIM 연구의 설계・시공・운영 단계별 토픽 모델링 분석: LDA와 BERTopic을 활용한 25년 시계열 연구동향 탐색
-
Baek-Jun Kim, Kweon-Hyoung Lee
김백준, 이권형
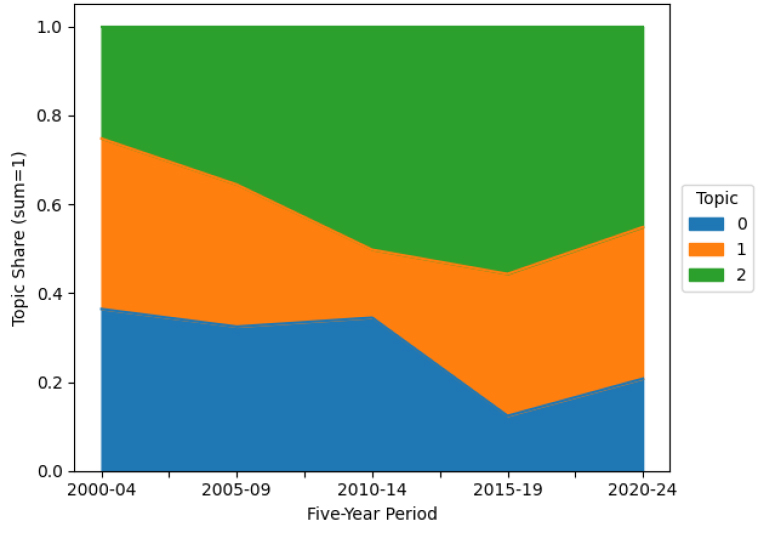
- This study analyzes the 25-year evolution of Building Information Modeling (BIM) research across design, construction, and operation phases through an integrated text …
- This study analyzes the 25-year evolution of Building Information Modeling (BIM) research across design, construction, and operation phases through an integrated text mining framework combining Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) and BERTopic methodologies. We examined 11,924 papers collected from the Korean Citation Index (KCI) and ScienceDirect databases spanning 2000~2024. The analysis reveals distinct developmental trajectories between research contexts: domestic studies demonstrate gradual, standards- based advancement with systematic phase expansion, while international research exhibits rapid innovation characterized by AI integration and digital twin convergence. Phase-based keyword analysis shows progressive expansion from design-centric applications to comprehensive construction and operation implementations. BERTopic clustering analysis indicates that domestic research maintains specialized topic segmentation with clear disciplinary boundaries, whereas international studies display highly interconnected thematic networks reflecting multidisciplinary integration. This study contributes a novel dual-methodology framework that systematically integrates temporal topic modeling with semantic clustering analysis, providing empirical insights for understanding BIM research evolution patterns and informing future research directions and policy development strategies. - COLLAPSE
-
Topic Modeling Analysis of BIM Research Across Design, Construction, and Operation Phases: A 25-Year Time-Series Study Using LDA and BERTopic
-
Research Article
-
Comparative Analysis of Marker-based and Model-based AR Registration for Bridge Pier Model
교각 모형을 대상으로 한 마커 및 모델 기반 AR 정합의 비교 연구
-
Yong-Ju Lee, SeongHyun Moon, Man-Woo Park
이용주, 문성현, 박만우
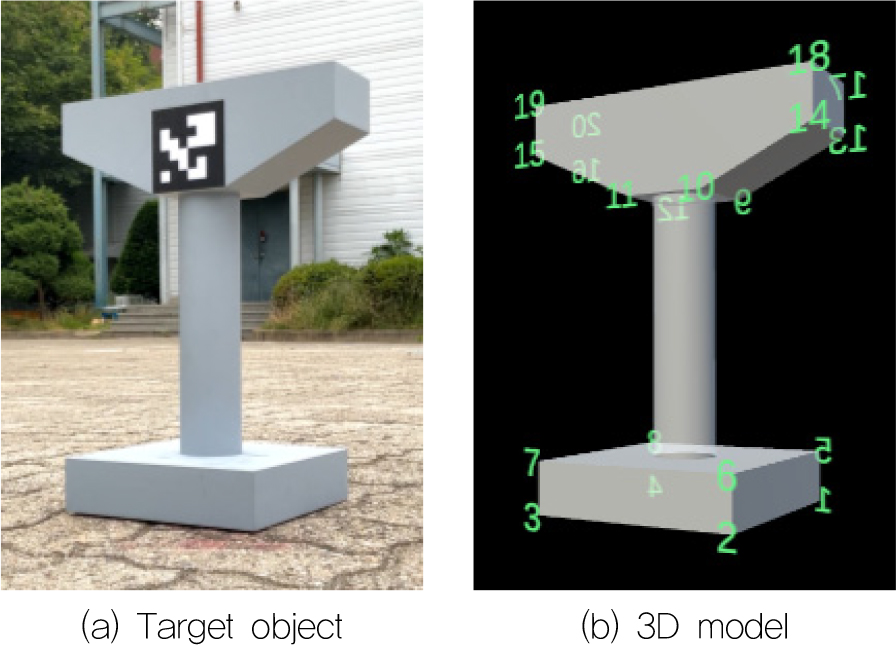
- Augmented Reality (AR) is emerging as a key technology for maximizing the value of digital assets like BIM on construction sites. The …
- Augmented Reality (AR) is emerging as a key technology for maximizing the value of digital assets like BIM on construction sites. The fundamental value of AR, however, depends on the precise registration of virtual models with the real world. While various AR registration techniques exist, there is a lack of empirical research that quantitatively compares their performance within the unique context of the construction industry. This study aims to bridge this gap by conducting a quantitative comparison of two predominant methods: the marker-based approach and a model-based markerless approach utilizing the commercial library. Through experiments using a bridge pier model, we quantitatively measured and analyzed the performance of each method during the critical phases of initialization and tracking. The results revealed a significant trade-off in the model-based approach: while it demonstrated robust and stable tracking performance under various viewing conditions once successfully initialized, its range for successful initialization was found to be remarkably narrow. In contrast, the marker-based method provided a more reliable initialization but was more susceptible to environmental conditions during tracking. The contributions of this paper are threefold. First, it provides an empirical, quantitative comparison of marker-based and model-based AR registration, offering objective data on their respective strengths and weaknesses for construction applications. Second, it empirically identifies the critical trade-off between the narrow initialization range and stable tracking performance inherent in the model-based method. Third, based on this comparative analysis, it suggests key factors—such as initialization success range and tracking stability under various conditions—that should be considered for designing future construction-specific performance evaluation metrics for AR systems. - COLLAPSE
-
Comparative Analysis of Marker-based and Model-based AR Registration for Bridge Pier Model
-
Research Article
-
Development of a Relational Database and LLM-Based Algorithm for Building Code Review in Early Design Stage
설계 초기단계 건축 법규 검토를 위한 관계성 DB 구축 및 LLM 기반 알고리즘 개발
-
Soonmin Hong, Bongkyun Park, Seungyeon Choo
홍순민, 박봉균, 추승연
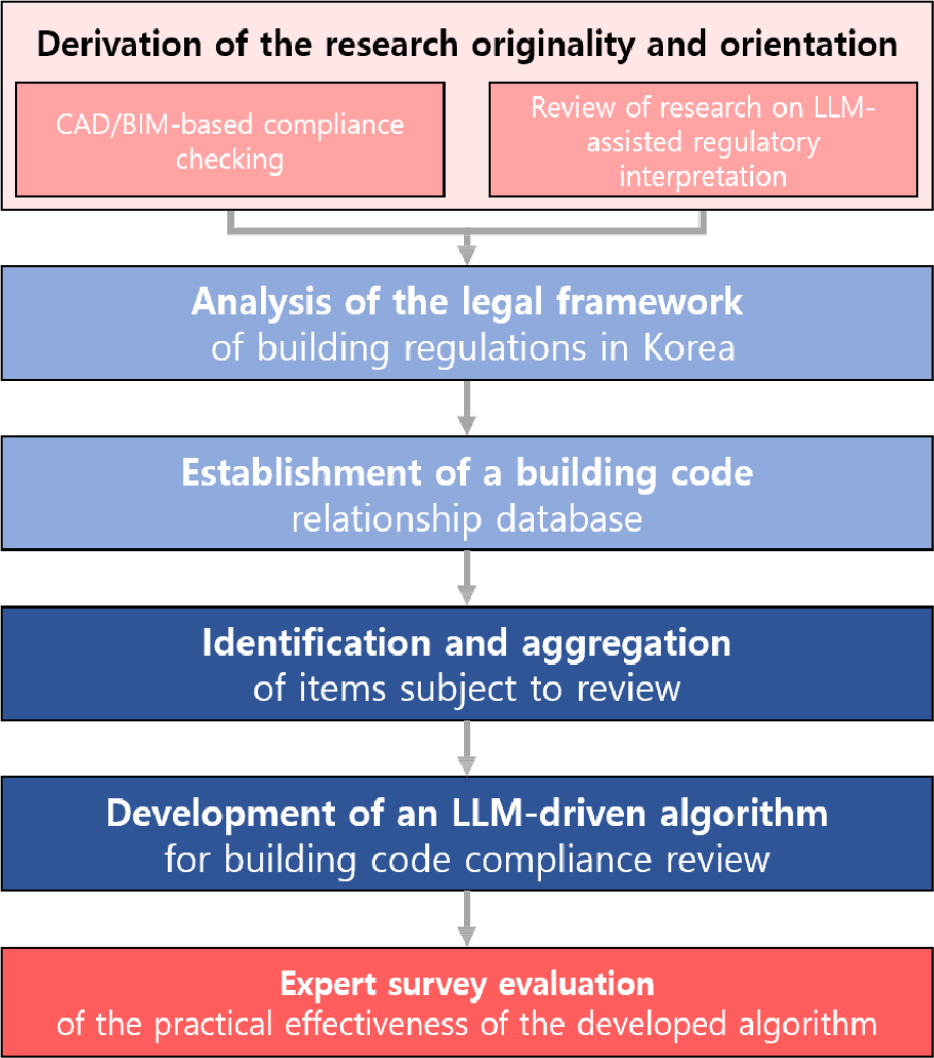
- Regulatory review in the early design stage is an essential yet complex task in architectural practice, as building codes often contain multi-layered …
- Regulatory review in the early design stage is an essential yet complex task in architectural practice, as building codes often contain multi-layered delegation and cross-referencing structures that are difficult to interpret systematically. Traditional CAD- and BIM-based rule-checking systems have improved efficiency, but they remain constrained by reliance on explicitly codified rules, which fail to capture contextual linkages across different provisions. To address these limitations, this study develops an algorithm that integrates a relational database (DB) of Korean building regulations with a large language model (LLM)-based question–answering module. The relational DB structures hierarchical and referential connections among legal clauses, while the LLM module generates adaptive responses that support legal interpretation and compliance review. The algorithm was implemented within an authoring tool environment that allows textual verification of regulatory results and volumetric visualization of building mass. This dual output enabled users not only to check whether key provisions were satisfied but also to understand their spatial impact on early-stage massing design. The relational DB was constructed by focusing on six critical categories affecting building form—building coverage ratio, floor area ratio, setback distances, landscape requirements, height limits, and parking provisions. These were encoded into a structured DB reflecting the hierarchical delegation and reference patterns of Korean building codes, and then connected to the LLM module to support context-sensitive Q&A-based analysis.Validation was conducted through a survey of 29 architectural practitioners with an average of 13 years of professional experience. Respondents evaluated the algorithm for effectiveness, accuracy, applicability, and user experience. Results confirmed the potential of the system to provide simplified yet reliable analysis that can support decision-making in the early design stage. At the same time, experts highlighted prerequisites for practical adoption, including real-time statutory updates, integration of local ordinances and district-unit plans, incorporation of site-specific conditions such as land slope and adjacency, and transparent reasoning logic that reveals the legal basis of each result. This study contributes academically by demonstrating the feasibility of combining relational data modeling and LLM-driven reasoning for building code review. Practically, it provides a pathway toward intelligent, adaptive, and explainable methods that can enhance both design productivity and compliance reliability, laying a foundation for future development of scalable and context-aware automated systems in architecture. - COLLAPSE
-
Development of a Relational Database and LLM-Based Algorithm for Building Code Review in Early Design Stage
-
Research Article
-
Configurable Point Cloud Processing Pipeline for Efficient Scan-to-BIM Conversion - Focusing on Terrain, Building, and Tree Object Segmentation -
Scan-to-BIM 효율화를 위한 구성 가능한 점군 처리 파이프라인 연구 - 지형, 건물, 수목 객체 분할을 중심으로 -
-
Taewook Kang
강태욱
- As digital twin and smart city technologies advance, the importance of 3D spatial information is increasing, and Scan-to-BIM technology plays a key …
- As digital twin and smart city technologies advance, the importance of 3D spatial information is increasing, and Scan-to-BIM technology plays a key role in converting the real world into a digital model. However, the process of segmenting and identifying objects required for BIM modeling from large-scale point cloud data still requires a lot of manual work, which is the main cause of lowering conversion efficiency. To solve this problem, this study proposes a configurable point cloud processing pipeline that allows users to flexibly combine processing steps and adjust parameters. The proposed pipeline sequentially segments terrain, buildings, and tree objects from point cloud data, and the algorithms and parameters of each processing step are controlled through an external configuration file. This paper analyzes the architecture, core algorithms, and configurability of this pipeline on the efficiency of Scan-to-BIM conversion. The analysis results show that rapid object segmentation is possible without repetitive coding work in response to various scan environments and object characteristics by simply adjusting parameters. This means that the reusability and automation level of the Scan-to-BIM preprocessing process can be increased, and the efficiency of the entire process can be improved by minimizing the intervention of workers. - COLLAPSE
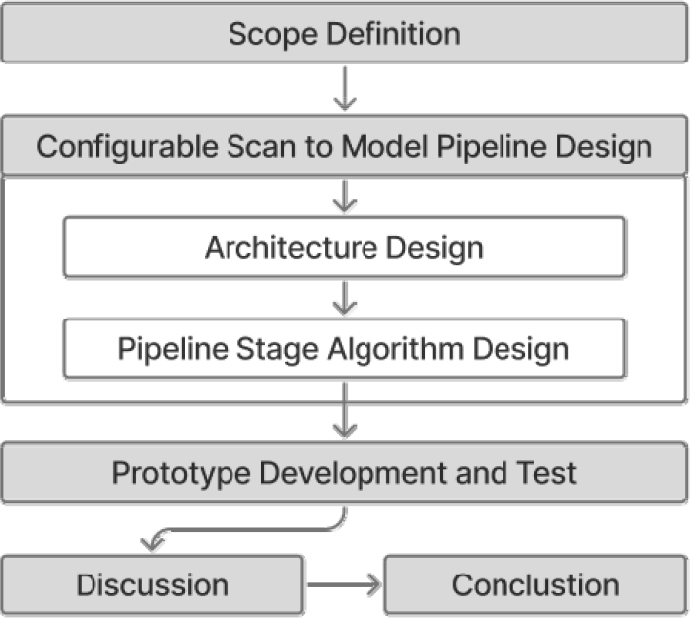
-
Configurable Point Cloud Processing Pipeline for Efficient Scan-to-BIM Conversion - Focusing on Terrain, Building, and Tree Object Segmentation -
-
Research Article
-
A Study on the Effectiveness of a BIM-Based Street Tree Management System
BIM 기반 가로수 관리 시스템의 효용성 연구
-
Hyunji Je, Yumi Lee, Hyoungjin Yoon
제현지, 이유미, 윤형진
- This study aims to analyze the effectiveness of BIM (Building Information Modeling) in the management of street tree data by comparing two …
- This study aims to analyze the effectiveness of BIM (Building Information Modeling) in the management of street tree data by comparing two case areas—Dongdaemun-gu and Gangbuk-gu in Seoul, South Korea. While Dongdaemun-gu employed the traditional method using CAD and Excel separately for spatial and attribute data, Gangbuk-gu adopted a BIM-based system using Revit. In the BIM approach, tree objects were modeled as parametric families, integrating attributes such as species, height, DBH, and planting status directly into the spatial model. The research found that BIM enhanced data consistency, minimized errors, and significantly improved the efficiency of information extraction and visualization. Notably, filtered data from the BIM model was exported to CAD format and used directly for municipal tree planting plans in Gangbuk-gu. This demonstrates BIM's potential not only for survey tasks but also as a practical tool for administrative decision-making and urban green infrastructure management. The study concludes that BIM can serve as a foundational platform for digital transformation in urban tree management, with possible scalability toward broader urban green infrastructure systems. - COLLAPSE
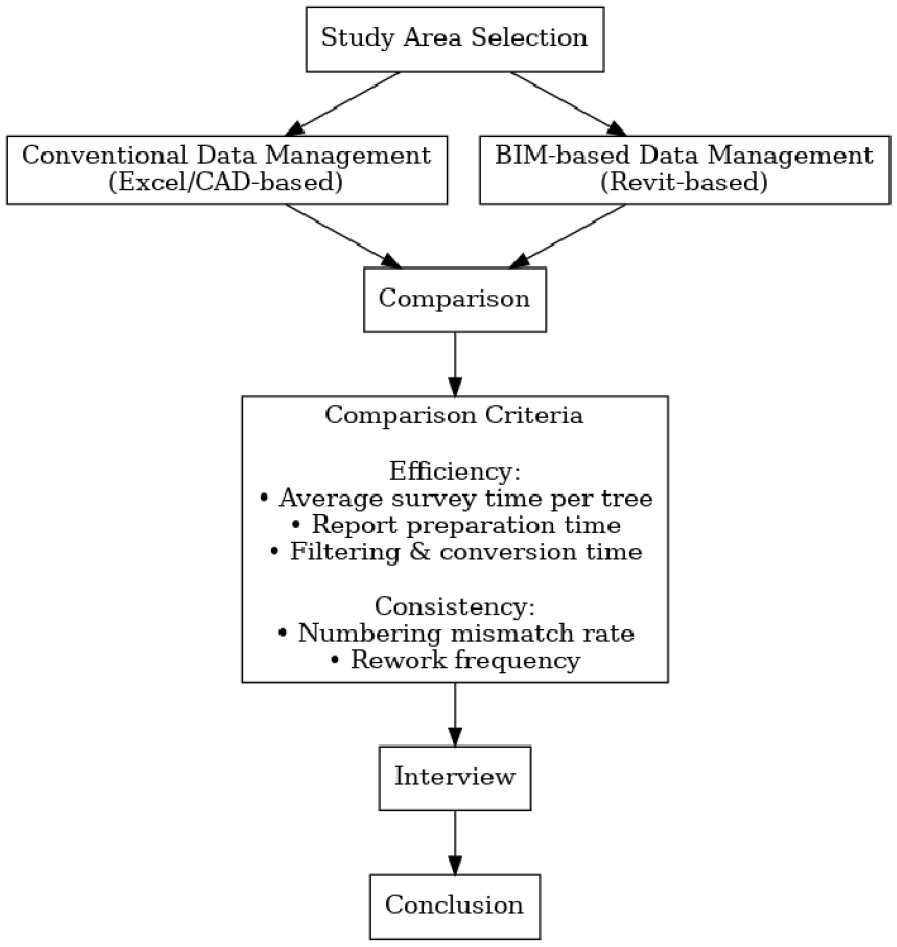
-
A Study on the Effectiveness of a BIM-Based Street Tree Management System
-
Research Article
-
A Study on the BIM-Based Design Change for Highway Drainage Facilities: Focus on Earthwork Section
BIM 기반 고속도로 배수시설 설계변경 체계 연구 - 토공구역 배수시설을 중심으로 -
-
Bong-Geun Kim, Junghwan Jang, Bo-Kyung Kim, Taekhee Han
김봉근, 장정환, 김보경, 한택희
- This study aims to develop a BIM-based framework to support design changes for drainage facilities installed within highway earthwork sections. The proposed …
- This study aims to develop a BIM-based framework to support design changes for drainage facilities installed within highway earthwork sections. The proposed framework consists of a standard BIM library, document templates, and automation modules for model placement and document generation. A BIM library encompassing 273 types of drainage facilities was developed based on the standard drawings of the Korea Expressway Corporation. The document templates for quantity take-off and cost estimation were formulated with reference to typical forms used in actual projects. Furthermore, automation modules were implemented using Dynamo to ensure that models, quantities, and costs in the associated documents remain consistently linked to the underlying BIM data. Application of the framework in a pilot project demonstrated that the time required to perform design change tasks was reduced by an average of 60–77%. Moreover, significant improvements were observed in the accuracy of quantity take-off, the elimination of manual input errors, and the efficiency of reviewing design change alternatives. - COLLAPSE
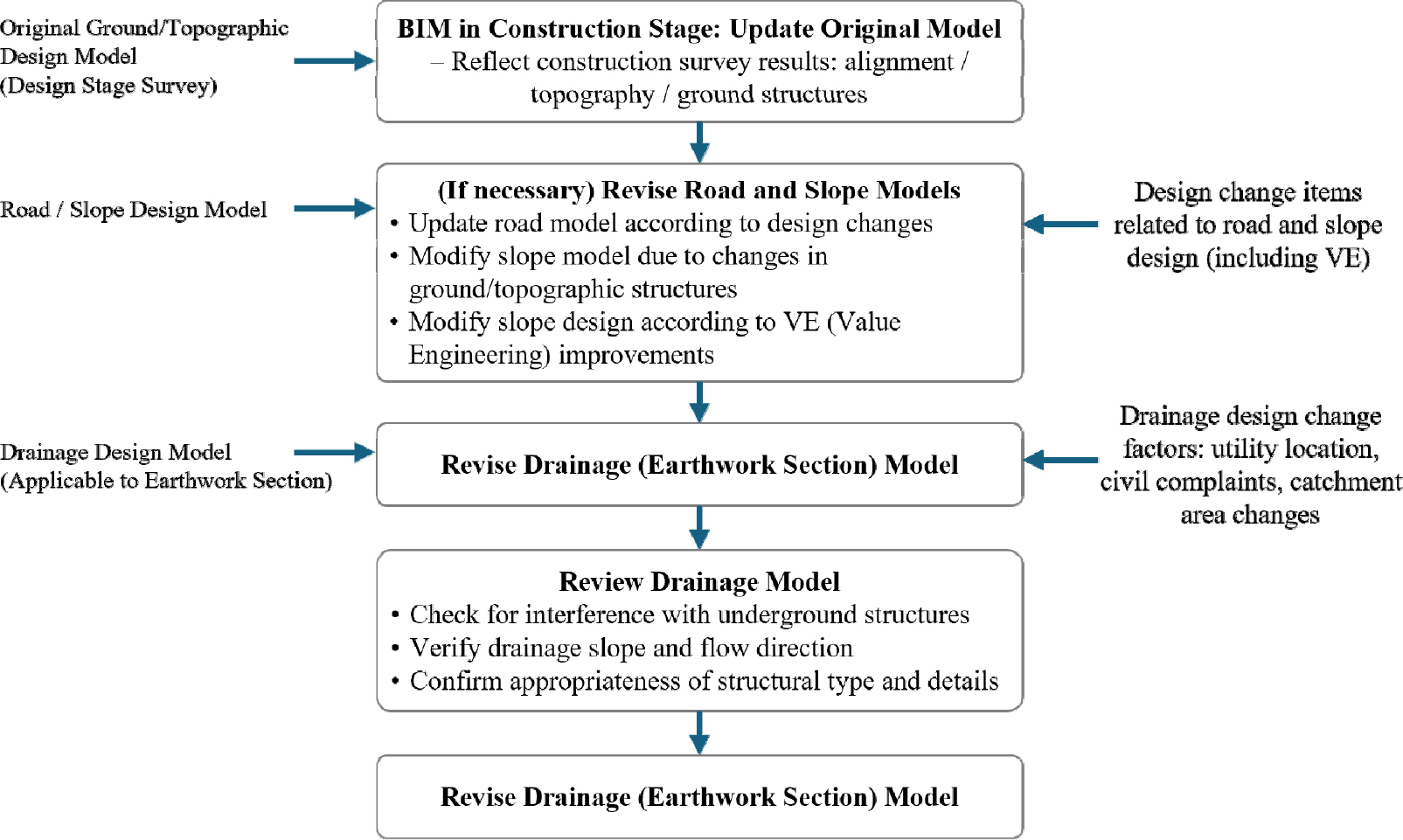
-
A Study on the BIM-Based Design Change for Highway Drainage Facilities: Focus on Earthwork Section
-
Research Article
-
Analysis of Deformation Behavior and Management Strategies of PSC Girders at Each Construction Stage
시공단계별 PSC 거더의 변형 특성 분석 및 관리기법
-
Jae-Woong Choi, Hyun-Min Kim, Jae-Min Sin
최재웅, 김현민, 신재민
- This study applied a measurement technique utilizing a total station and reflector target Sheets to precisely analyze the deformation characteristics of prefabricated …
- This study applied a measurement technique utilizing a total station and reflector target Sheets to precisely analyze the deformation characteristics of prefabricated bridge girders at each construction stage. Displacement was measured at four stages: pre-tensioning, girder erection, upper deck construction, and load testing. The structural stability was assessed by comparing and analyzing the displacement with allowable deflection and transverse curvature standards. This enabled quantitative identification of deformation patterns at each stage, and the early detection of abnormal behavior confirmed the effectiveness of this measurement technique in preventing safety accidents during construction. This study highlights the importance of deformation management at each construction stage and suggests the potential for future development of automated displacement analysis and AI-based predictive maintenance systems. - COLLAPSE

-
Analysis of Deformation Behavior and Management Strategies of PSC Girders at Each Construction Stage
-
Research Article
-
Automatic Registration Method between BIM and Point Cloud Data for Construction Accuracy Analysis
시공정밀도 분석을 위한 BIM과 포인트클라우드 데이터의 자동 정합 방안
-
Hyeon-Su Lim, Yu-Sin Lee, Seok-Heon Yun
임현수, 이유신, 윤석헌
- This study proposes an automatic registration process between Building Information Modeling (BIM) and point cloud models to enhance construction accuracy analysis. Specifically, …
- This study proposes an automatic registration process between Building Information Modeling (BIM) and point cloud models to enhance construction accuracy analysis. Specifically, the proposed method utilizes Z-axis and centroid alignment based on RANSAC, global registration using Fast Point Feature Histograms (FPFH), and fine registration via a 2D plane-based Iterative Closest Point (ICP) algorithm. To validate the performance of the automated process, registration results were visualized using heatmaps to analyze spatial error distributions. Furthermore, the effectiveness of the proposed technique was quantitatively evaluated by comparing the global registration stage with the complete automatic registration process using point-to-point distance error histograms and statistical metrics, including Mean, Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), and Standard Deviation. Experimental results using corridor data from a target building demonstrated that the proposed method reduced the mean error by over 80% compared to existing methods, achieving high registration precision. These findings suggest that the proposed approach improves both the efficiency and accuracy of BIM–point cloud integration, thereby streamlining construction quality control tasks while enhancing inspection precision. - COLLAPSE
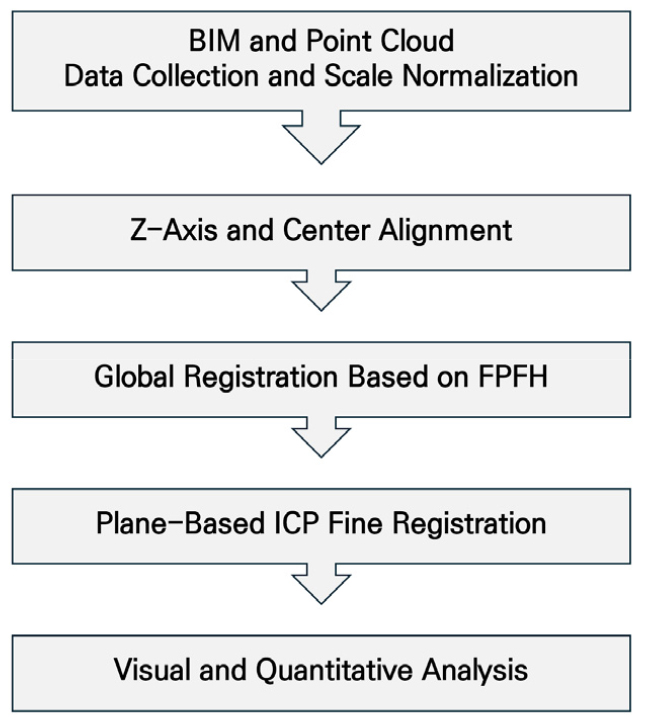
-
Automatic Registration Method between BIM and Point Cloud Data for Construction Accuracy Analysis



 Journal of KIBIM
Journal of KIBIM








